What are database structures? What are different types of database structures and what are their functions?
Concepts:
- What are database structures?
- They are the organization and layout of data within a database system.
- They are essential for efficiently storing, retrieving, and managing data.
- An operational database system keeps the data organized and allowing users to access the data.
- What are different types of database structures and what are their functions?
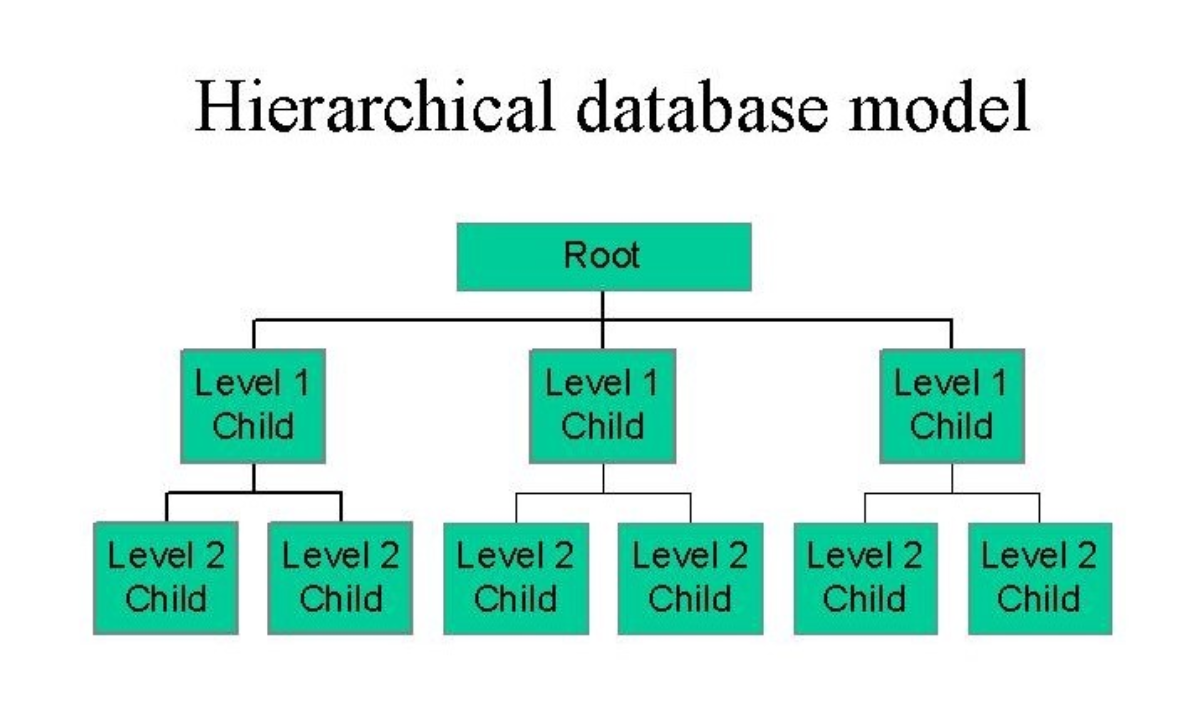
- Hierarchical databases have a parent-child family tree structure. It has a rigid and complex navigation structure but offers easy acess and quick querying time.
- Relational databases store data in discrete tables that can be joined together using foreign keys.
- Non-relational databases don't use the tabular schema of rows and columns and came into use due to increasingly complex modern web applications.
- Object-oriented databases store and manage objects on a database server's disk, and is unique because associations between objects can persist.
Application:
An example of hierarchical databases is the Windows registry. An example of relational databases is a user table containing data about users joining with a Purchases table containing data about the purchases users have made. Non-relational databases include MongoDB and Redis. An example of object-oriented databases is where the query language contructs native objects through a chosen SDK in the MongoDB Realm.
Quiz:
Question 1: What are the 4 types of database structures?
Hierarchical Databases, Relational Databases, Non-Relational Databases, and Object Oriented Databases
Question 2: How are object oriented databases unique?
Object oriented programming and the querying of data across complex relationships is fast and powerful because associations between objects can persist.
Question 3: What is the difference between relational and non-relational databases?
Relational stores data in discrete tables, which can be joined together by fields known as foreign keys, while non-relational don't use the tabular schema of rows and columns.